I decided to publish few articles where I will document how to create a hybrid network between your local network and Azure (using some chip routers) and finaly how to create a VM in Azure as a part of your network. This is the Part 1 of whole proces and here is covered how to create Virtual network in Microsoft Azure.
In this article I will explain the complete step-by-step guideline how to create a network in Azure, site to site VPN from your local network to Azure and finally how to create an Azure VM connected to your local domain.
There are few things that you have to know:
- local subnet,
- IP of local router,
- IP of local DNS server (in your AD domain).
First we need to create virtual network in Azure. This will be a part of our network, but as we will connect to this network via VPN, it must be on a different subnet.
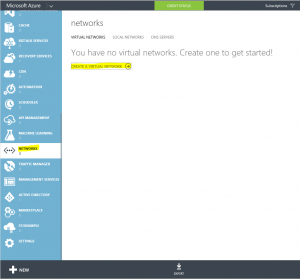
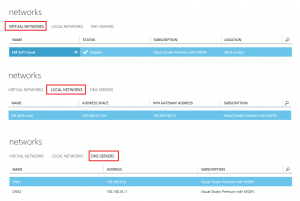
To create a Virtual network, you have to login into an Azure portal, select Networks and then Create a virtual network.
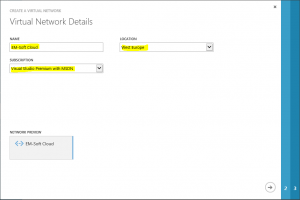
This will launch a wizard for creating network and this are the steps that you have to perform. First just give a name to network and chose a location and subscription. Be careful with choosing a location. Later you will be able to use VPN only to virtual machines, in the same location where the network is.
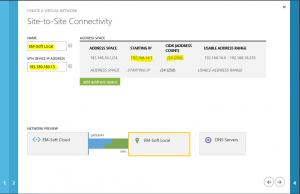
On the second screen you have to enter some data about connectivity. As we said at the beginning, the VPN will be site to site, so you have to select this one. DNS servers will be used to resolve names in this network and as we want to add a virtual machine, which is a part of our Active directory, we should be able to resolve it in our AD. This is the reason why specified DNS servers have to be our local DNS servers from local AD (not public DNS!).
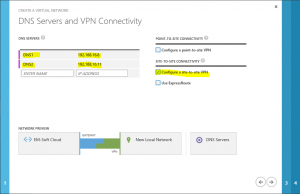 Next step is to specify our local network. You have to specify the name of the network.
Next step is to specify our local network. You have to specify the name of the network.
VPN device IP address is a public address of your router, from which you will establish the connection to Azure.
In address space you have to specify all of your private networks, from which you want to establish connections to Azure.
All of this data are needed by Azure for determination of routes and connectivity.
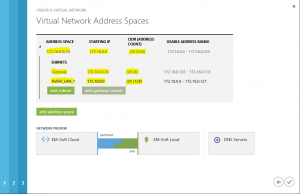
In the last step, you have to define the address space used in Azure. This is a private IP address space and has to be different from your local IP address space.
The rules to define are the same as those you have when you create VPN between two local sites, but there are some more settings:
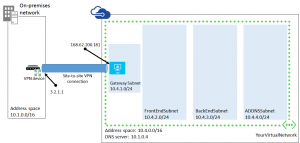
- Address space defines the whole address space that you can use as a part of Azure virtual network. Any subnet, which is a part of this network, must be created as a part of this space.
- Gateway subnet: this subnet is responsible to have connectivity outside of Azure. In this subnet will be located a router, which will act as endpoint of VPN tunnel. Do not use this subnet to create virtual machines in it.
- Subnet: you have to create at least one subnet. This will be the address space where you will create virtual machines. In many cases will be enough one subnet, but if you have to build a larger deployment, isolations of VM or similar things, maybe you will need more than one.
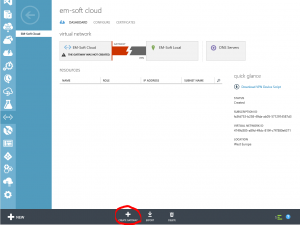
With this steps you created a set of network settings that include Azure virtual network, local network and DNS setting. When you finish this steps, your Azure network is ready to use, but don’t forget to create a gateway. This one is necessary to establish a VPN connection.
If you want to use this network in a combination with your local network, you have to create a gateway. This is an IP which will act as an end point of VPN Tunnel. For creating the gateway, you have another wizard; it is not complicated, but it could take time (30 minutes or more).
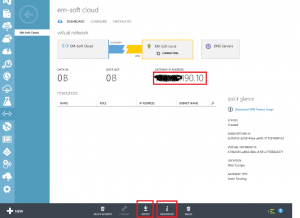
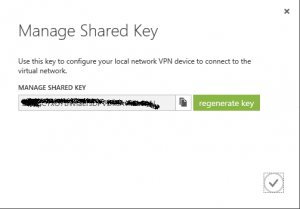
Click on create gateway on the bottom of the page, and use Static routing if you have a static IP address. After the creation of the gateway is complete, you will have an IP address of the gateway. This is the IP address that you will have to write into your local router as the endpoint of VPN. The only thing that is missing now, is a shared key. You can read it by clicking Manage Key button on the bottom of the page. Write down this key, because you will need it later in the router configuration.
If you have a router model (like Cisco…) that is supported by Azure, you can export data to configure it directly from the portal with clicking “Export” button. In all other cases, you will need to estabilish VPN manually – here you will need to press the Manage Key button.
For establishing the connection to Azure network successfully, you will need a preshared key and a gateway IP address (showed at previous and next picture). I recommend, to write them down into some file or on a paper.