It could happen. I saw this issue couple of times, not only on domain controllers, but also on other domain joined computers.
The cause of this problem is the Network Location Awareness service. We know, that this service is recognising network location based on gateway and is trying to locate AD server thru port 389. Well, when gateway is changed or no server connection true port 389 is available, we have a new network location – by default it is Public.
Anyway, it can happened that NLA service starts before the AD services are started (or before DC is reachable on a non DC server). In this case, we will have public network profile on DC or domain joined computers. If firewall is enabled, most of network services will not run as the firewall for the Public profile is almost closed.
We have few possibilities to solve this situation. Maybe the most simple way is to restart the server, but I don’t know if I can restart the server at this moment and what was the original cause of the problem – maybe it will reappear. The second option is to disable / reenable the NIC adapter and in most cases, it will solve the issue. We will get the same result if we just restart the NLA service – this is a better way.
In some cases, you cannot connect to the computer for some reason. In this case, I use PowerShell remote session to solve the problem.
Here are the steps:
Enter-PSSession ComputerName (establish connection to computer with the problem)
Get-NetConnectionProfile (this will show you your current location profile – if this is the source of the problem, the location will not be Domain)
Restart-Service nlasvc (this cmdlet will restart NLA service; after this step you should see Domain network profile)
Get-NetConnectionProfile (just to check if the solution works)
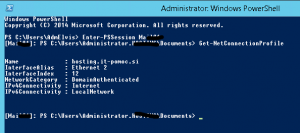
Exit-PSSession (disconnect form the remote computer)
Based on my experience, this solution works always. Some administrators also suggest to change start option for NLA service to Automatic (Delayed Start). I am not sure if this is a good solution; be careful with it. Maybe you can do it in cases where this error is frequent (better: search for the original cause and solve the problem)