Everyone of us want to stop Cryptolocker and similar programs. It seems that it is really a nightmare for all admins. Anyway, to stop Cryptolocker and any unwanted program, you have to be aware, that this will bring limitations to your system, which are not always welcome.
How does Cryptolocker work?
We have 5 phases of Cryptolocker infections:
- Installation: The software is delivered to your computer via download or E-Mail attachment and the user click on it. The executable is now installed, the registry keys are set and we are ready to go to the next phase.
- Contacting headquarters: the computer is contacting criminal headquarters for registration, so it will prepare all environment for phase 3.
- Creating keys: headquarter and client are now identifying each other and are ready to “handshake” and create two keys for encryption.
- Encryption: Cryptographic keys are now established and the encryption can begin. It depends on version, but almost all files on all local and shared drives where you have permissions will be encrypted.
- Extortion: The screen with a guide how much and where to pay is displayed. There is displayed also how much time you have for payment. If you will not pay in time, the headquarter key will be deleted and you will not be able to decrypt files. The payment is every day higher – so if you want to pay, do it immediately.
To prevent a large number of unwanted software, the first step to do is always remove LocalAdmin permissions and turn on UAC. This two actions will put you in situation where user will not be able to install any application and write to system crucial folders. Also have your system always up to date. And I don’t mean only OS, but include all applications installed (we know attacks to Java, Adobe FlashPlayer, Microsoft Office…).
Of course this is not enough as a lot of bed guys know how to elevate permissions or are using different folders (for example AppData is used for Cryptolocker), but been a LocalAdmin is a great way to become a victim. I suggest to all home users and system administrators to use two different accounts – one for daily use and the second for administrator tasks.
Well, the real way to prevent Cryptolocker is blocking the execution of exe files in AppData folder. You can do this with group policy in AppLocker or in software restriction policy. This are steps for basic protection with AppLocker:
- Create new GPO for Cryptolocker prevention
- Edit new created GPO
- Expand Computer configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security settings > System Services
- Enable “Application Identity” service and set it to automatic startup mode
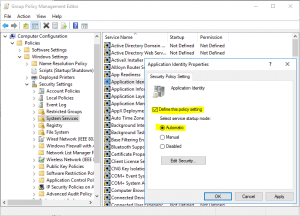
- Go down to Application Control Policies and expand to AppLocker
- In “Configure role enforcement enable Executable rules and make them in Enforce mode (I suggest you, to run them in Audit mode for week or two and analyze logs before enforcing them – just to find legal applications which can be blocked)
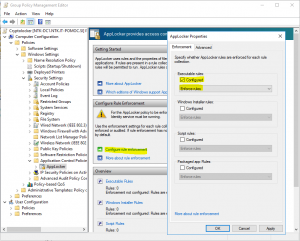
- Expand AppLocker and click to Executable rules
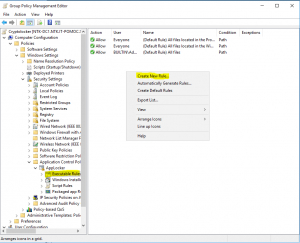
- Right click in action pane and create Default Rules
- Right click in action pane and create New Rule
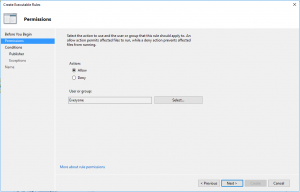
- In Permissions on Action set Allow for Everyone
- In Conditions select that is Publisher rule
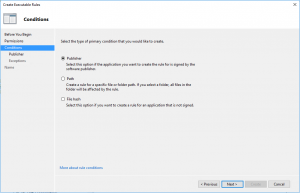
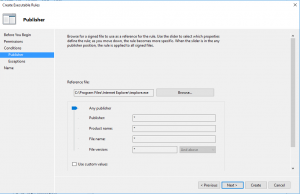
- In Publisher, just browse one file (in my case was Internet Explorer) and go with slider up to Any publisher
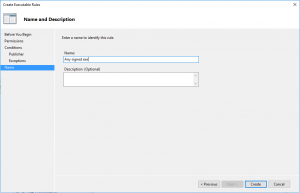
- Give the name to the rule
So, this is about AppLocker, but we have still a lot of work to do. There is a big surface for attack if users are local admin. To prevent this, configure Restricted groups in GPO by using Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security settings > Restricted Groups.
Apply this GPO to all computers and the first step is done.
GPO is a good way to prevent Crypto, but be aware that Crypto is evolving and you have to evolve with him. And preventing Crypto with GPO means that executable is already in your system – maybe you have to prevent it before is downloaded or received with mail. For this step you will need the application firewall, good antivirus in file system and in mailing system.
But still you can do something with chip devices with closing outgoing ports 83, 846, 777, 997, 1604, 9001, 9003, 444, 9052, 8443, 7777, 9003 and 25254. This ports are used to communicate with headquarter servers to obtain a certificate for encryption (maybe exist also other ports or will be added / changed during the time). If you will close this ports, the system will not be able to retrieve a certificate for encryption and the encryption will not be able to begin. Be careful on notebooks because the users will bring their notebooks at home and the encryption will be successful.
As you can see, there are a lot of ways to prevent Cryptolocker, but you have to prevent it. When you have it, it is too late – think about it now!
And for home users? Well we cannot forget them. They have a lot of pictures and documents on their computers – practically a whole life and is a really big impact to lose all this material.
I suggest you a software from FoolishIT. It is free and it is working good (but if you want to keep it up to date, give those few Euros to the author – he is doing his job well!).
Additional reading:
https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/mmpc/2015/01/13/crowti-update-cryptowall-3-0/
http://www.crowdstrike.com/blog/4-0-another-brick-in-the-cryptowall/
http://researchcenter.paloaltonetworks.com/2015/02/analysis-cryptowall-3-0-dyre-i2p/
https://tools.cisco.com/security/center/viewAlert.x?alertId=36338
